Цель:
Цель:
Оценить эффективность и переносимость тоцилизумаба в многоцентровом рандомизированном двойном слепом плацебо-контролируемом исследовании у рефрактерных взрослых пациентов с дерматомиозитом (ДМ) и полимиозитом (ПМ).
Методы:
Тридцать шесть пациентов с вероятным или определенным ДМ/ПМ были включены в 6-месячное клиническое исследование фазы 2B и рандомизированы 1:1 для получения тоцилизумаба (8 мг/кг внутривенно) или плацебо каждые 4 недели в течение 24 недель. Подходящие субъекты с ДМ имели сыпь, либо аутоантитела, ассоциированные с миозитом, либо подтвержденный диагноз ПМ.
Активное заболевание определялось по крайней мере тремя из шести показателей аномального набора основных показателей (CSMs), включая ручное мышечное тестирование (MMT)-8 баллов менее 136/150. Если оценка MMT-8 была больше 136, то требовался кожный балл 3 или более (визуальная аналоговая шкала 10 см) наряду с тремя дополнительными аномальными CSMs, указывающими на активность заболевания.
Первичная конечная точка сравнивала общий балл улучшения (TIS) между обеими группами с 4 по 24 неделю. Вторичные результаты включали время до достижения общего минимального балла улучшения (TIS), изменения в основных показателях (CSMs), время до ухудшения, стероид-ассоциированные эффекты, долю субъектов, отвечающих более строгим критериям улучшения, и результаты безопасности.
Результаты:
Не было никакой существенной разницы (Р= 0,86) в TIS в течение 24 недель между группами тоцилизумаба и плацебо. Вторичные конечные точки времени до улучшения (минимальное, умеренное или значительное), времени до ухудшения, изменений CSMs, результаты безопасности и стероид-ассоциированные эффекты также существенно не различались между группами.
Заключение:
Тоцилизумаб был безопасен и хорошо переносился, но не соответствовал результатам первичной или вторичной эффективности при рефрактерном ДМ и ПМ в этом 24-недельном исследовании фазы 2B.
Chester V. Oddis, Howard E. Rockette, Lei Zhu and others
https://doi.org/10.1002/acr2.11493
DOI 10.1002/acr2.11493
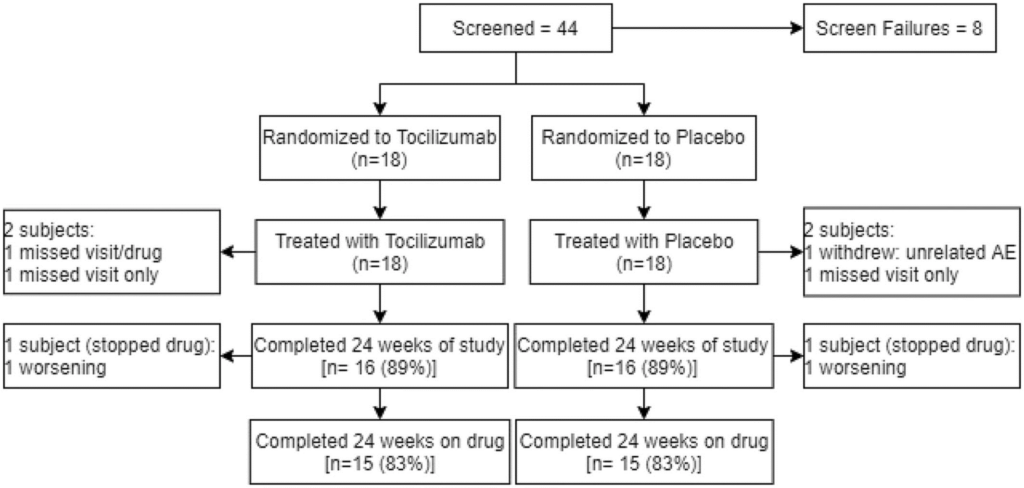
Figure 1. Participant flow diagram. Participant flow diagram of subjects enrolled in tocilizumab in myositis trial. AE, adverse event.
Table 1. Baseline demographic and clinical characteristics and core set measures by treatment group.
| Characteristic | Tocilizumab | Placebo | P value |
| (n = 18) | (n = 18) | ||
| Caucasian, n (%) | 12 (67) | 14 (78) | 0.71a |
| Age (y), mean (range) | 54.3 (31.3-83.4) | 50.4 (21.5-70.7) | 0.41b |
| Female, n (%) | 15 (83) | 13 (72) | 0.69a |
| IIM subset, n (%) | 0.30 | ||
| PM | 8 (44) | 5 (28) | |
| DM | 10 (56) | 13 (72) | |
| Prednisone dose (mg/dayc), mean (SD) | 8.3 (7.5) | 17.8 (20.5) | 0.07b |
| Patients on prednisone, n (%) | 12 (67) | 15 (83) | 0.44a |
| Patients taking nonglucocorticoid IS and/or immunomodulatory agents, n (%) | 15 (83) | 15 (83) | 1.00a |
| Mtx | 4 (22) | 6 (33) | |
| Mtx + Aza | 1 (6) | 1 (6) | |
| Mtx + IVIg | 1 (6) | 1 (6) | |
| Mtx + MMF | 0 (0) | 1 (6) | |
| MMF | 6 (33) | 0 (0) | |
| Aza | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | |
| Aza + IVIg | 0 (0) | 1 (6) | |
| Tacrolimus | 1 (6) | 2 (11) | |
| IVIg | 1 (6) | 3 (17) | |
| Patients with positive myositis autoantibodies, n (%) | 8 (44) | 10 (56) | 0.51 |
| Antisynthetase | 0 (0) | 4 (22) | |
| Anti-TIF1-γ | 2 (11) | 1 (6) | |
| Anti-Mi-2 | 2 (11) | 2 (11) | |
| SRPd | 2 (11) | 0 (0) | |
| HMGCRe | 0 (0) | 1 (6) | |
| MJ/NXP-2 | 1 (6) | 1 (6) | |
| MDA-5 | 1 (6) | 0 (0) | |
| Ro60 | 0 (0) | 1 (6) | |
| MMT-8 score, mean (SD) | 126.7 (15.3) | 132.8 (11.5) | 0.19b |
| Global assessment by VAS (0-10 cm scale), mean (SD) | |||
| Physician | 5.1 (1.7) | 4.7 (1.4) | 0.47b |
| Patient | 6.1 (2.1) | 5.4 (2.4) | 0.37b |
| HAQ disability index (range 0-3), mean (SD) | 1.3 (0.7) | 1.3 (0.6) | 0.94b |
| Muscle enzyme (xULN)f, median (IQR) | 9.1 (1.0-9.8) | 1.5 (1.0-2.4) | 0.41g |
| Extramuscular score by VAS (0-10 cm scale), mean (SD) | 3.3 (2.5) | 3.3 (1.6) | 0.95b |
Abbreviations: Aza, azathioprine; DM, dermatomyositis; HAQ, health assessment questionnaire; HMGCR, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; IIM, idiopathic inflammatory myopathy; IQR, interquartile range; IS, immunosuppressive; IVIg, intravenous immunoglobulin; MDA, melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5; MMF, mycophenolate mofetil; MMT, manual muscle testing; Mtx, methotrexate; NXP-2, anti-nuclear matrix protein-2; PM, polymyositis; SRP, signal recognition particle; VAS, visual analog scale; xULN, times the upper limit of normal.
a Fisher’s exact test P value (χ2 tests were performed for all other categorical variables listed in the above table to generate the P values). b Two sample t test P value. c Prednisone dose (mg/day) in subjects taking any dose of prednisone. d Signal recognition particle. e 3-hydroxy-3-methyl glutaryl-CoA reductase. f Upper limit normal. g Wilcoxon test P valu
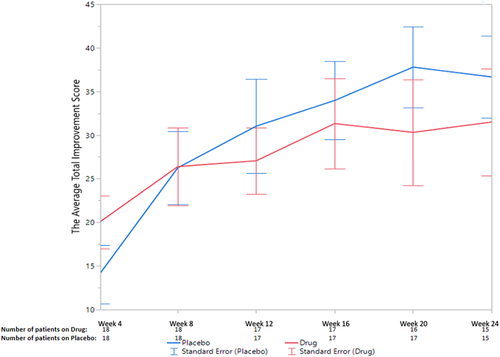
Figure 2. The average total improvement scores of the placebo and treatment groups at each of the six follow-up visits. Figure 2. The average total improvement scores of the placebo and treatment groups at each of the six follow-up visits.
Table 2. Change in core set measures from baseline to week 24
| Core set measures | Tocilizumab | Placebo | |||
| Baseline | Week 24 | Baseline | Week 24 | ||
| (average) | (average) | (average) | (average) | P valuea | |
| Extramuscular global assessment (MDAAT) | 3.3 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 1.9 | 0.49 |
| Physician global disease activity | 5.1 | 3.9 | 4.7 | 2.3 | 0.19 |
| Muscle enzyme (xULNb) | 9.1 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 0.22 |
| Patient global disease activity | 6.1 | 4.2 | 5.4 | 4.1 | 0.07 |
| MMT-8 | 126.7 | 135.1 | 132.8 | 139.7 | 0.82 |
| HAQ DI | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 0.60 |
Abbreviations: HAQ DI, Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index; MDAAT, Myositis Disease Activity Assessment Tool; MMT-8, manual muscle testing. a GEE model P values, for comparing the overtime changes (4-24 weeks) in each core set measure between the two treatment groups. b Times upper limit normal.

Figure 3. Change in glucocorticoid dose between baseline and completion of the 24-week treatment phase. TCZ, tocilizumab.
Randomized Trial of Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Refractory Adult Polymyositis and Dermatomyositis
Objective:
To assess the efficacy and tolerability of tocilizumab in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in refractory adult patients with dermatomyositis (DM) and polymyositis (PM).
Methods:
Thirty-six subjects with probable or definite DM/PM were enrolled in a 6-month phase 2B clinical trial and randomized 1:1 to receive tocilizumab (8 mg/kg intravenously) or placebo every 4 weeks for 24 weeks. Eligible subjects had either a DM rash, a myositis-associated autoantibody or an adjudicated PM diagnosis. Active disease was defined by at least three of six abnormal core set measures (CSMs), including a manual muscle testing (MMT)-8 score of less than 136/150.
If the MMT-8 score was greater than 136, then a cutaneous score of 3 or more (10 cm visual analogue scale) was required along with three additional abnormal CSMs indicating disease activity. The primary endpoint com-pared the Total Improvement Score (TIS) between both arms from week 4 to 24. Secondary outcomes included time to meeting minimal TIS improvement, changes in CSMs, time to worsening, steroid-sparing effect, proportion of subjects meeting more stringent improvement criteria, and safety outcomes.
Results:
There was no significant difference (P= 0.86) in the TIS over 24 weeks between tocilizumab and placebo arms. The secondary endpoints of time to improvement (minimal, moderate, or major), time to worsening, CSM changes, safety outcomes, and steroid-sparing effect were also not significantly different between arms.
Conclusion:
Tocilizumab was safe and well tolerated but did not meet the primary or secondary efficacy outcomes in refractory DM and PM in this 24-week phase 2B study.