Информация
Информация
Тофусная форма подагры — это тяжелая форма подагры, которая приводит к образованию крупных узелков (тофусов), в пораженных суставах и окружающих тканях. Подагрические тофусы в позвоночнике имеют целый ряд проявлений, которые часто имитируют другие патологии и могут быть плохо отличимы от более распространенных патологических процессов.
Клинический случай
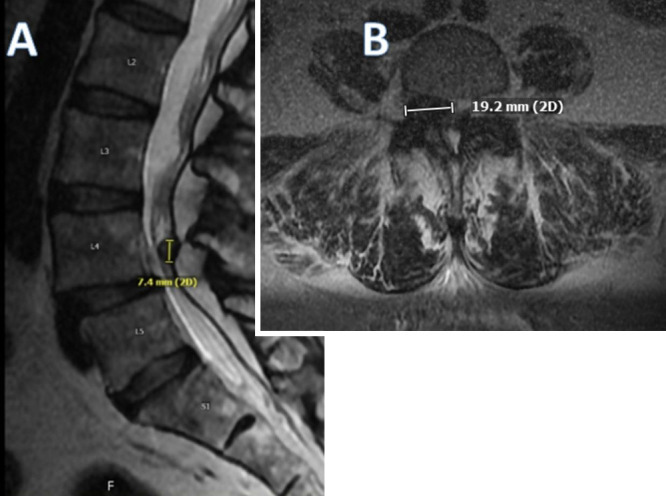
47-летняя женщина с хронической болезнью почек, ожирением, подагрой, воспалительным полиартритом и рассеянным склерозом поступила с 6-месячной болью в пояснице и поясничной радикулопатией, отдающей в правую нижнюю конечность. Магнитно-резонансная томография поясничного отдела выявила стеноз правого фораминального канала и спондилолистез на уровне L4-L5.
Отмечено интраспинальное экстрадуральное образование рядом с правым L5 и выходящим справа L4 нервными корешками. Была выполнена двусторонняя декомпрессивная ламинэктомия, фасетэктомия и фораминотомия на уровне L4-L5.
В форамине было обнаружено кальцифицированное, белое как мел образование, которое патологоанатомы определили как подагрический тофус. После операции пациентка подтвердила устранение симптомов, наблюдавшихся до операции, которые не вернулись при последующем наблюдении.
Выводы
Сообщения о подагрических отложениях, сдавливающих спинной мозг, в современной литературе встречаются относительно редко. Хотя определение подагрического тофуса может быть подтверждено только гистологически, история болезни может служить полезным диагностическим инструментом.
Patrick Chang, Brandon C Rogowski, Khaled Abdel Aziz, Rosh Bharthi, Lance Valls, Nathan Esplin, Richard W Williamson
Journal of Neurosurgery: Case Lessons. Volume 6, Issue 26, December 2023
Foraminal stenosis and radiculopathy secondary to tophaceous gout: illustrative case
Background:
Tophaceous gout is a severe form of gout that results in the formation of large nodules, or tophi, in the affected joints and surrounding tissues. Gouty tophi in the spine have a constellation of presentations that often mimic other pathologies and may not be easily discernable from more common pathologic processes.
Observations:
A 47-year-old female with a history of chronic renal disease, obesity, gout, inflammatory polyarthritis, and multiple sclerosis presented with 6 months of low-back pain and lumbar radiculopathy affecting the right lower extremity. A lumbar magnetic resonance imaging study revealed right foraminal stenosis and spondylolisthesis at levels L4−5.
An intraspinal extradural mass was noted adjacent to the traversing right L5 and exiting right L4 nerve roots. A bilateral decompressive laminectomy, facetectomy, and foraminotomy of L4−5 was performed. A calcific, chalky-white mass was discovered in the foramen, and pathology determined the specimen to be a gout tophus. Postoperatively, the patient endorsed the resolution of her preoperative symptoms, which have not returned on follow-up.
Lessons:
Reports of gouty depositions compressing the spinal cord in the current literature are relatively rare. Although the diagnosis of gouty tophi can only be confirmed histologically, patient history may serve as a helpful diagnostic tool.